Page 64 - Demo
P. 64
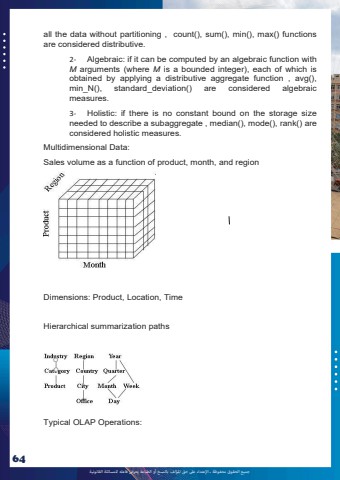
%u062c%u0645%u064a%u0639 %u0627%u0644%u062d%u0642%u0648%u0642 %u0645%u062d%u0641%u0648%u0638%u0629 %u0640 %u0627%u0625%u0644%u0639%u062a%u062f%u0627%u0621 %u0639%u0649%u0644 %u062d%u0642 %u0627%u0645%u0644%u0624%u0644%u0641 %u0628%u0627%u0644%u0646%u0633%u062e %u0623%u0648 %u0627%u0644%u0637%u0628%u0627%u0639%u0629 %u064a%u0639%u0631%u0636 %u0641%u0627%u0639%u0644%u0647 %u0644%u0644%u0645%u0633%u0627%u0626%u0644%u0629 %u0627%u0644%u0642%u0627%u0646%u0648%u0646%u064a%u062964all the data without partitioning , count(), sum(), min(), max() functions are considered distributive. 2- Algebraic: if it can be computed by an algebraic function with M arguments (where M is a bounded integer), each of which is obtained by applying a distributive aggregate function , avg(), min_N(), standard_deviation() are considered algebraic measures. 3- Holistic: if there is no constant bound on the storage size needed to describe a subaggregate , median(), mode(), rank() are considered holistic measures. Multidimensional Data: Sales volume as a function of product, month, and region Dimensions: Product, Location, Time Hierarchical summarization paths Typical OLAP Operations: