Page 117 - Demo
P. 117
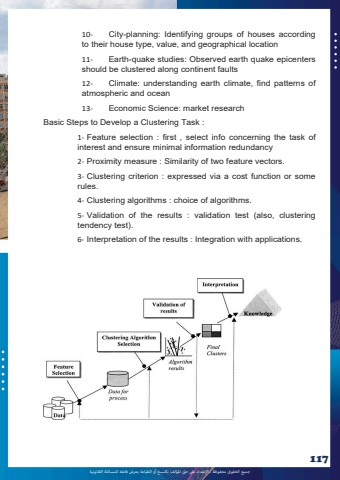
%u062c%u0645%u064a%u0639 %u0627%u0644%u062d%u0642%u0648%u0642 %u0645%u062d%u0641%u0648%u0638%u0629 %u0640 %u0627%u0625%u0644%u0639%u062a%u062f%u0627%u0621 %u0639%u0649%u0644 %u062d%u0642 %u0627%u0645%u0644%u0624%u0644%u0641 %u0628%u0627%u0644%u0646%u0633%u062e %u0623%u0648 %u0627%u0644%u0637%u0628%u0627%u0639%u0629 %u064a%u0639%u0631%u0636 %u0641%u0627%u0639%u0644%u0647 %u0644%u0644%u0645%u0633%u0627%u0626%u0644%u0629 %u0627%u0644%u0642%u0627%u0646%u0648%u0646%u064a%u062911710- City-planning: Identifying groups of houses according to their house type, value, and geographical location 11- Earth-quake studies: Observed earth quake epicenters should be clustered along continent faults 12- Climate: understanding earth climate, find patterns of atmospheric and ocean 13- Economic Science: market research Basic Steps to Develop a Clustering Task : 1- Feature selection : first , select info concerning the task of interest and ensure minimal information redundancy 2- Proximity measure : Similarity of two feature vectors. 3- Clustering criterion : expressed via a cost function or some rules. 4- Clustering algorithms : choice of algorithms. 5- Validation of the results : validation test (also, clustering tendency test). 6- Interpretation of the results : Integration with applications.