Page 31 - Demo
P. 31
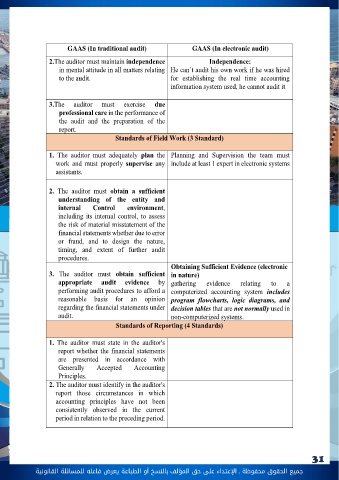
جميع الحقوق محفوظة ـ اإلعتداء عىل حق املؤلف 31 بالنسخ أو الطباعة يعرض فاعله للمسائلة القانونيةD) Generalized Audit Software (GAS): A tool used by auditors to automate various audit tasks. Pre-prepared generalized programs used by auditors and are not ‘client specific, written to be used on different types of computer systems. GAS (As: Audit Command Language (ACL) and Interactive Data Extraction and Analysis (IDEA)) involves using specialized software to assist in the auditing of the system. Audit firms prefer it as it allows them to achieve the goal without interfering with the client system. Phase 4: Completion of the audit and issuing audit report:The auditor must widen the scope of the documentation of audit process to account for documenting electronic evidences and trails and method of holding documentation files differs from paper documents to electronic ones However, the audit report issued (four types discussed earlier) does not change with IT environment applicable. What are the Applicable standards in traditional and IT Audit?Auditing depends on (GAAS) The generally acceptable standards of audit, which classify standards to 3 main categories detailed as Follows: A.General standards B.Field work standards C.Reporting Standards GAAS (In traditional audit) GAAS (In electronic audit) General Standards (3 Standards) 1. The auditor must have adequate technical training and proficiency to perform the audit. Training and Proficiency (In the field of IT and auditing electronic system not only accounting and auditing wiseCompetence and capabilities must be directly related to information technology and controls in a computerized environment