Page 107 - Demo
P. 107
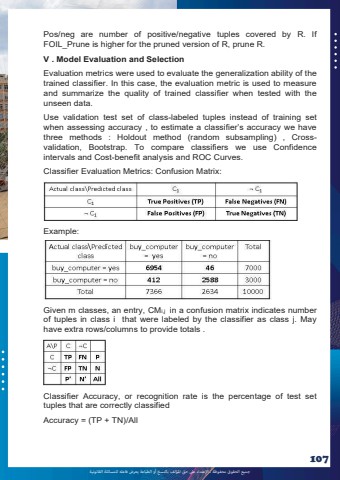
%u062c%u0645%u064a%u0639 %u0627%u0644%u062d%u0642%u0648%u0642 %u0645%u062d%u0641%u0648%u0638%u0629 %u0640 %u0627%u0625%u0644%u0639%u062a%u062f%u0627%u0621 %u0639%u0649%u0644 %u062d%u0642 %u0627%u0645%u0644%u0624%u0644%u0641 %u0628%u0627%u0644%u0646%u0633%u062e %u0623%u0648 %u0627%u0644%u0637%u0628%u0627%u0639%u0629 %u064a%u0639%u0631%u0636 %u0641%u0627%u0639%u0644%u0647 %u0644%u0644%u0645%u0633%u0627%u0626%u0644%u0629 %u0627%u0644%u0642%u0627%u0646%u0648%u0646%u064a%u0629107Pos/neg are number of positive/negative tuples covered by R. If FOIL_Prune is higher for the pruned version of R, prune R. V . Model Evaluation and Selection Evaluation metrics were used to evaluate the generalization ability of the trained classifier. In this case, the evaluation metric is used to measure and summarize the quality of trained classifier when tested with the unseen data. Use validation test set of class-labeled tuples instead of training set when assessing accuracy , to estimate a classifier%u2019s accuracy we have three methods : Holdout method (random subsampling) , Crossvalidation, Bootstrap. To compare classifiers we use Confidence intervals and Cost-benefit analysis and ROC Curves. Classifier Evaluation Metrics: Confusion Matrix: Example: Given m classes, an entry, CMi,j in a confusion matrix indicates number of tuples in class i that were labeled by the classifier as class j. May have extra rows/columns to provide totals . Classifier Accuracy, or recognition rate is the percentage of test set tuples that are correctly classified Accuracy = (TP + TN)/All